Dedicated to the millions of Diabetics worldwide
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a condition in which the body cannot handle glucose appropriately after absorption. DM is associated with fasting, high blood sugar, and high glucose after meals. DM can be either Type 1 or Type 2.
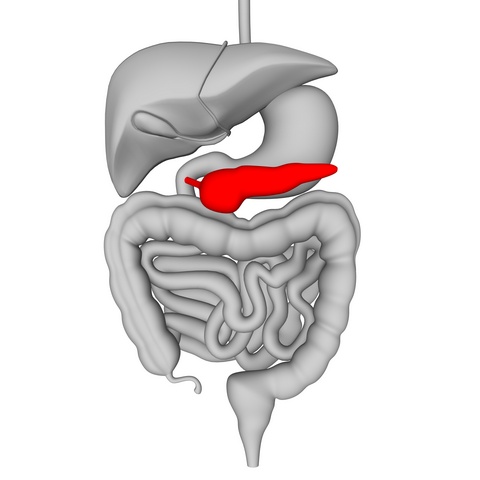
Type 1 DM is due to a lack of insulin production in the pancreas. This is more common in young individuals <20s and is due to an autoimmune process.
Type 2 diabetes is due to insulin resistance (insulin is not as effective as it should be), impaired insulin secretion, increased glucose production by the liver, increased glucagon (a hormone that causes the release of glucose from the liver) release.
NOTE: Insulin resistance means that the cells are not able to use insulin in the usual way. Insulin resistance is almost undoubtedly genetic in origin. The beta cells in the pancreas where insulin is produced have to overwork to produce more insulin to overcome the insulin resistance, leading to beta-cell exhaustion, leading to beta cells’ death, later resulting in decreased insulin production and higher blood sugar.
Type 2 Diabetes has a strong genetic link, usually associated with other affected family members. This genetic link and environmental factors such as poor diet and decreased physical activity predispose to Type 2 Diabetes. No single genetic defect accounts for Type 2 Diabetes; it is due to multiple gene defects.
Normal
Metabolism of Glucose
After digestion, food is broken down to glucose in the gut. It is then absorbed into the bloodstream. Glucose is carried in the blood to every cell of your body. Cells need glucose for their energy needs. To get inside the cell, glucose needs insulin’s help. If one has insulin resistance as in Type 2 Diabetes or an absolute lack of insulin as in Type 1 Diabetes, the glucose has difficulty entering the cell. Thus cells are starved of energy, but blood glucose tends to be very high.
To correct this problem in Type 2 Diabetes, we need to reduce insulin resistance. This can be achieved
Be Informed. Get In Control. Prevent.
Better late than never
Coming Soon!
Available Aug 16, 2019
Diabetes Cure
Be Informed. Get In Control.

My Writing Blog
Follow Along
Screening For Diabetes
Diabetes Screening and Diagnosis Who Should Be Screened? Everyone aged 45 and older should be screened for diabetes or glucose abnormalities every three years. However, individuals at higher risk should begin screening earlier and more frequently—ideally once a year....
Disaster Planning
you never know When Disaster Occurs Emergency Preparedness for People with Diabetes When natural disasters or emergencies strike—such as hurricanes, floods, wildfires, or power outages—being prepared can protect your health and even save your life. Everyone with...
Neuropathy
Important to reduce all risk factors Diabetic neuropathy Diabetic neuropathy, a common complication of diabetes, encompasses various types of nerve damage resulting from prolonged high blood sugar levels. It can affect different parts of the nervous system, leading to...
Contact Us
The newsletter is only sent if there are any new blogs or articles added.